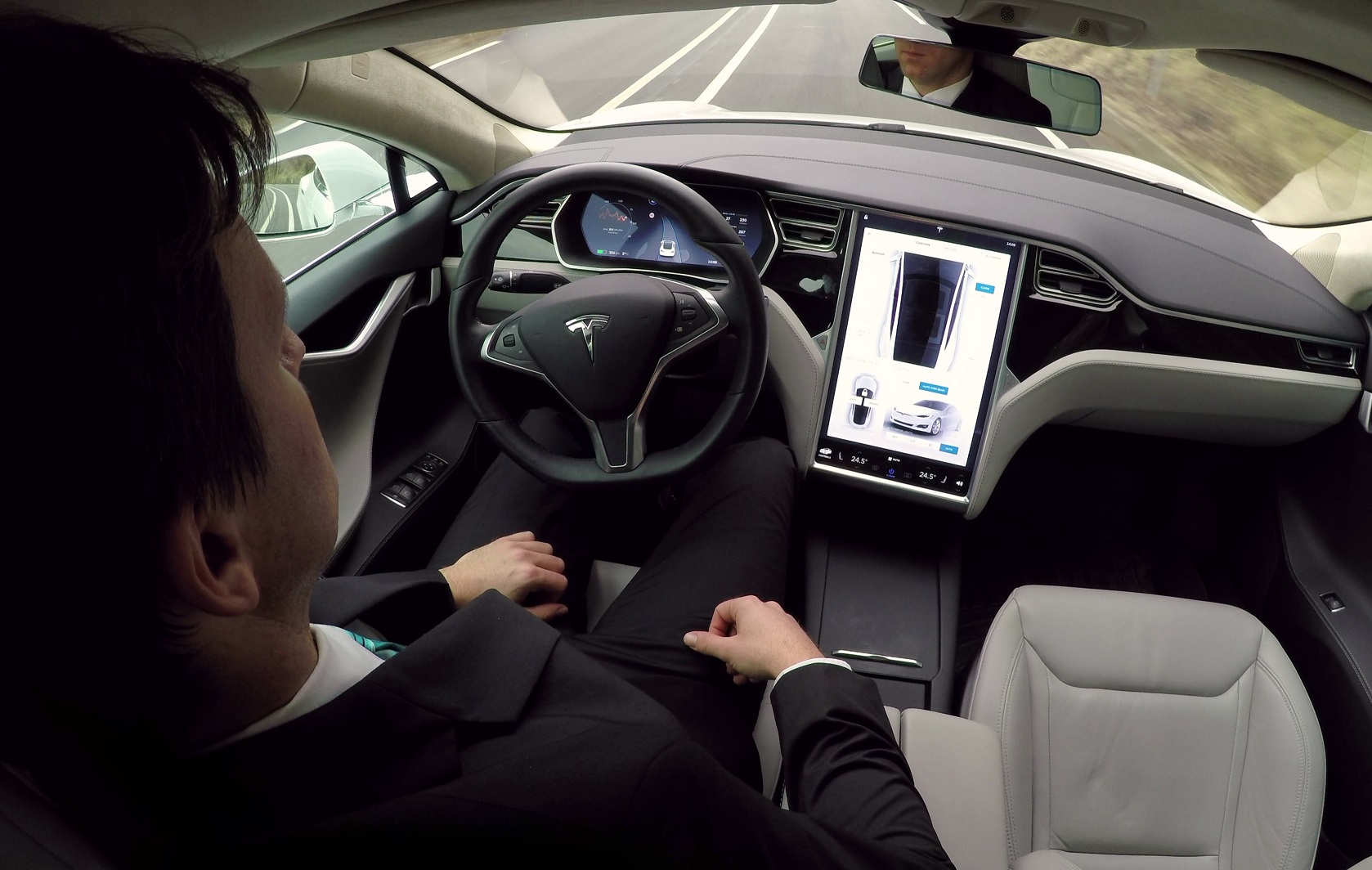
Everything You Need To Know About Self-Driving Cars
With autonomous vehicles like the Tesla Model S and Cadillac Escalade, it seems like automotive dreams of our favorite sci-fi media have come to fruition.
But how exactly do these cars work? Are they truly self-driving? And most importantly, are they safe? Let’s find out.

What Is An Autonomous Vehicle?
A broad definition of an autonomous vehicle would be a vehicle that has technology to sense driving conditions like pedestrians and traffic while also enabling the car to change speed or course without being controlled by a person.
Autonomous vehicles are also called self-driving vehicles.
 BP63Vincent, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
BP63Vincent, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
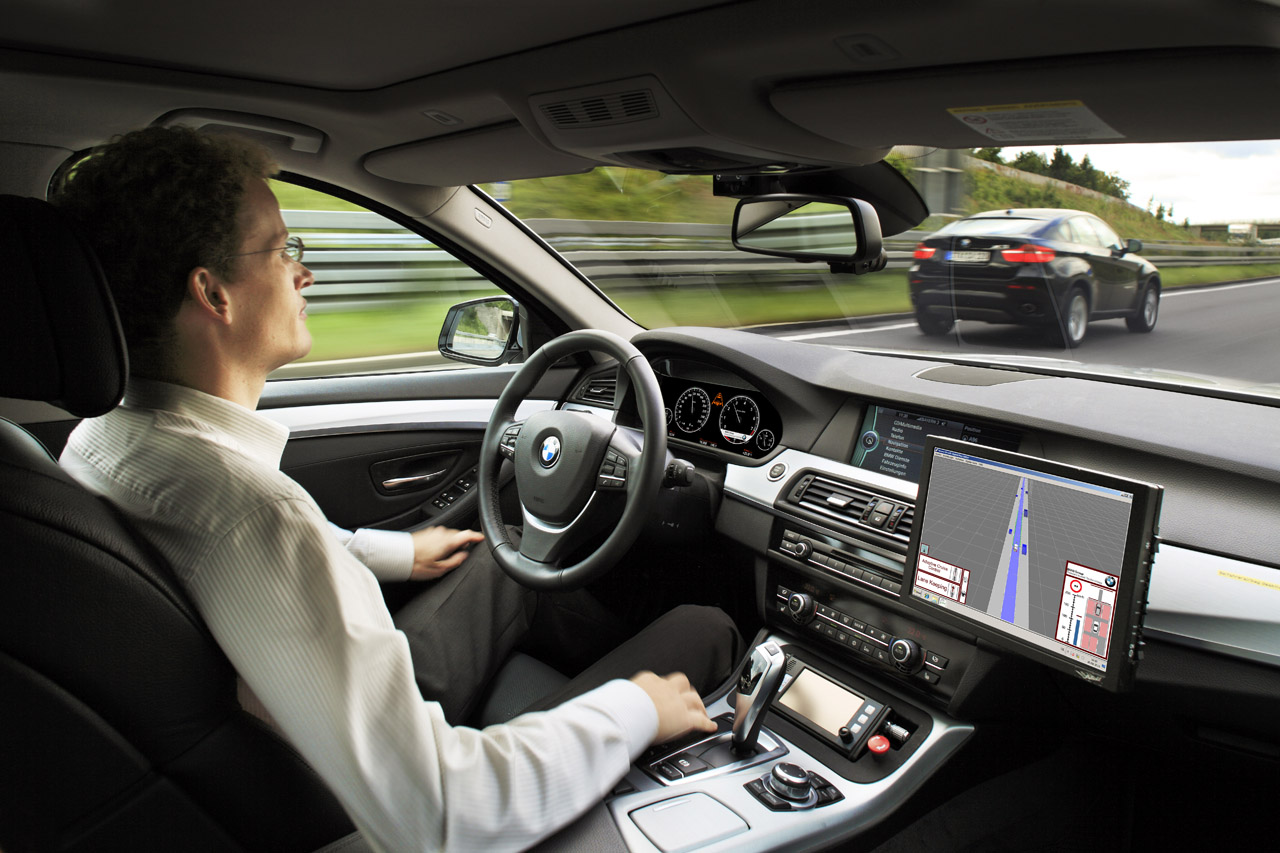
How Does It Work?
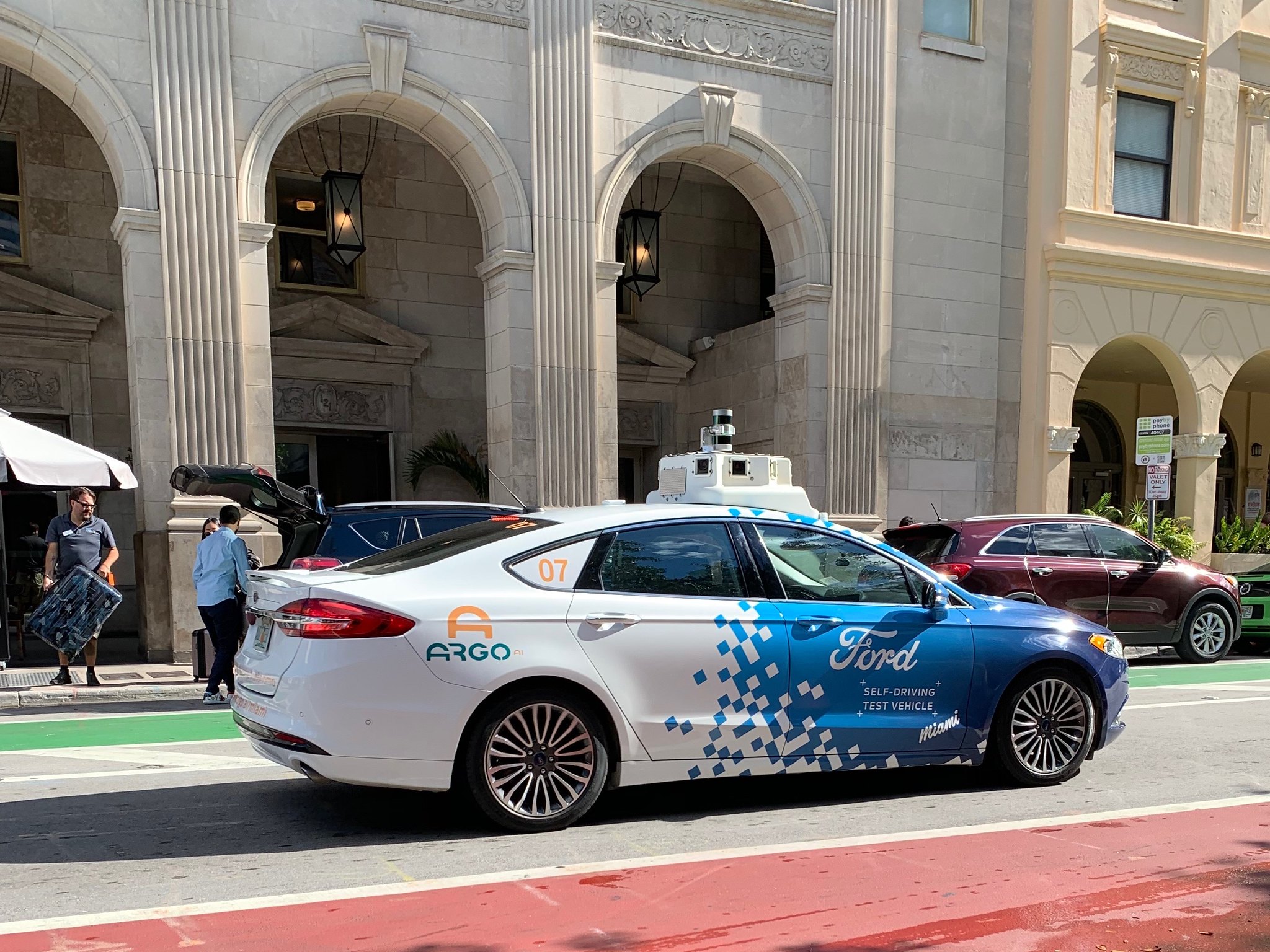
Self-driving cars can sense what’s happening around them with three main features: radar, cameras, and laser-based light detection (LiDar).
These three features act like eyes for the car and they send data to sophisticated on-board processors and software, which tells the car how to react.
How Does It Work? (cont’d)
The sensors can detect a wide range of things, like curbs, pedestrians, and even lane markings.
Sensors on autonomous cars can be great safety features, but they aren’t foolproof. Certain weather conditions like snow or rain can diminish how effectively the car can sense lane markings or curbs.
SAE International’s Definition
While there are several cars on the market that have self-driving features, the world has yet to see a fully autonomous vehicle.
According to SAE International, one of the world’s leading organizations of automotive engineers, there are six different levels of autonomous driving, and only the final level is truly self-driving.
Level 0
Levels 0 to 2 are driver support features and lack the sophistication of higher levels that are deemed to have self-driving capabilities.
At Level 0, the car may have features like lane departure warnings and a blind-spot alert system, but the driver is in full control of how the car reacts to its surroundings.
Level 1
Cars at Level 1 may have responsive safety features that are slightly autonomous. For example, some cars are equipped with a lane-keeping system that will center the car if the driver is veering too much to one side.
Level 2
Most new cars are equipped with Level 2 autonomous features. At Level 2, the tech features of the car communicate with each other, and can also support simultaneous active features.
Adaptive cruise control is an example of Level 2 technology, as it can adjust the car’s speed to maintain a specific distance from the driver ahead while also keeping the car in the center of the lane.
Level 2 (cont’d)
Most new cars that boast self-driving technology are classified as Level 2. Tesla’s Full Self-Driving and General Motor’s Super Cruise are Level 2 autonomous tech.
While these systems are incredibly responsive, drivers still need to be focused on the road when using these features and be ready to re-take control of the vehicle at any moment.
Level 3
At Level 3, a vehicle starts to become fully autonomous. A Level 3 autonomous car is able to drive itself under certain conditions.
These cars can sense curves in the road, control speed and steering, and follow a specified route. However, even with this improved responsiveness, drivers still need to be alert and ready to take control.
Level 3 (cont’d)
Honda and Mercedes are the only companies that have created Level 3 autonomous driving technology.
Honda was the first to up the ante with their 100 Legend Flagship. Unveiled in 2021, this car can only be leased in Japan.
Level 3 (cont’d)
Mercedes-Benz is the only automaker to offer Level 3 autonomous driving features in America. Their Drive Pilot system will be rolled out in California and Nevada and will be available in the 2024 S-Class and EQS Sedan.
The system can control driving up to a certain speed, allowing drivers to take their eyes off the road and focus on something else, like watching a movie.
 Krivosheev Vitaly, Shutterstock
Krivosheev Vitaly, Shutterstock
Level 4
At Level 4, a car can drive itself on a specified route on known roads. The driver doesn’t have to retake control at any time, so these cars often lack foot pedals or steering wheels.
Right now, Level 4 autonomous driving technology is being tested in certain rideshare companies, but it has yet to be approved for extensive use.
Level 5
Level 5 is the final point of evolution for self-driving cars. These cars can drive themselves on any road, in any conditions, and don’t require any driver input. They have no need for steering wheel or pedals.
Level 5 is the stuff of sci-fi, and as of now, any Level 5 autonomous driving systems are purely theoretical.
Self-Driving Cars In The Real World
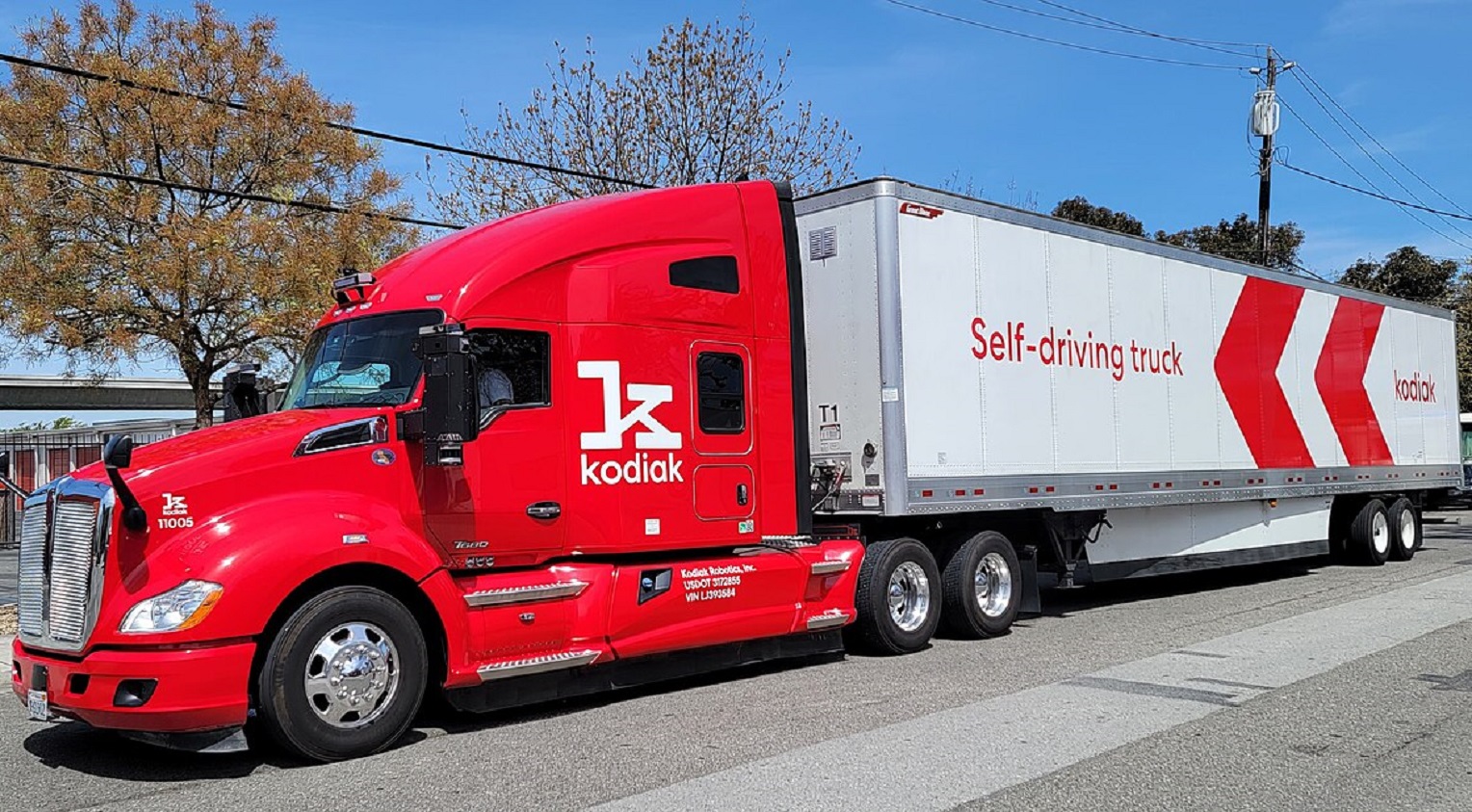
Though they’re not quite at Level 3, some companies use fleets of trucks that are self-driving. These trucks often have a “safety driver” on board but some have no driver at all.
While many of these trucks are restricted to warehouse grounds, some are used to transport goods on major roads.
 Phil Whitehouse, CC BY 2.0, Wikimedia Commons
Phil Whitehouse, CC BY 2.0, Wikimedia Commons
Self-Driving Cars In The Real World (cont’d)
Gatik and Kodiak Robotics are two companies that use self-driving trucks on certain routes. While they hope to soon run the trucks without a safety driver, the lack of human control in today’s self-driving cars isn’t without risk.
 Votpuske, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
Votpuske, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
Is Self-Driving Technology Safe?
While autonomous driving features are reliable for the most part, there have been serious cases of this tech going wrong.
Most recently, Tesla had to recall more than 2 million vehicles after their autopilot software was deemed unsafe by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration.
 VanderWolf Images, Shutterstock
VanderWolf Images, Shutterstock
Is Self-Driving Technology Safe? (cont’d)
Tesla isn’t the only company to suffer a setback because of faulty autonomous software.
One of General Motors’ subsidiaries, Cruise, had to put a pause on making their self-driving cars, after one was involved in an accident with a pedestrian.
They're Not Going Anywhere
Despite the recent safety incidents, self-driving cars are here to stay. May Mobility recently unveiled a new transit service that uses fully autonomous cars.
The service is only available in Arizona, but their fleet of self-driving Toyota minivans has proven to be safe and effective—even with no safety driver onboard.
Advantages Of Self-Driving Cars
Companies like May Mobility prove there is a future for fully autonomous vehicles. And even with concerns for safety, there are advantages to using self-driving cars.
In general, these cars offer a new level of convenience for drivers as they do other things during the commute. They can also improve safety on the road.
Advantages Of Self-Driving Cars (cont’d)
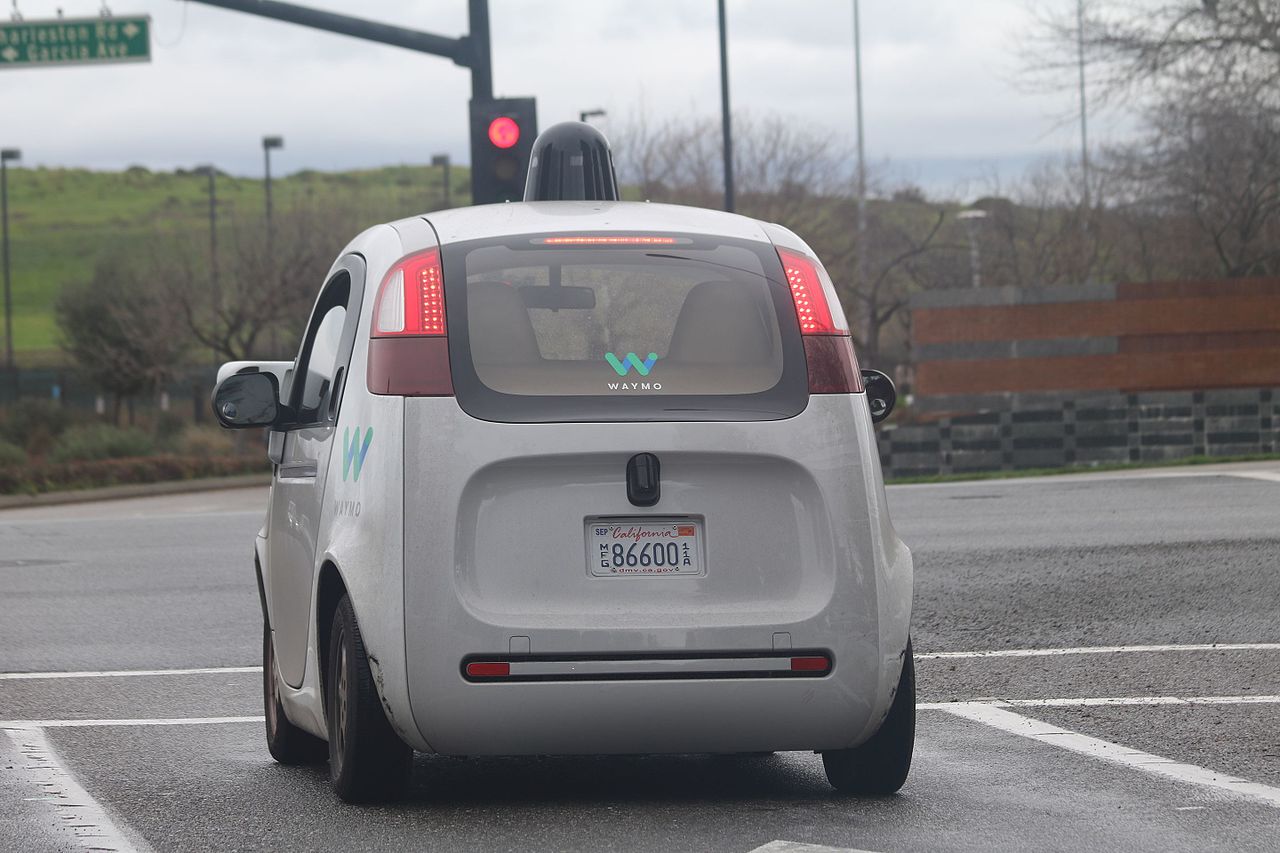
According to the National High Traffic Safety Administration, today’s self-driving cars do help reduce traffic congestion and accidents.
That's because the automated driver assistance system (ADAS) in many new cars helps drivers anticipate imminent threats and work to avoid them.
 Grendelkhan, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
Grendelkhan, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
Advantages Of Self-Driving Cars (cont’d)
Self-driving cars are also a great option for people who can’t drive, such as the elderly or those with disabilities.
Autonomous vehicles offer more mobility than conventional public transportation, making it easier for people to run errands and get to important appointments.
Environmental Considerations
In addition to less congestion, autonomous vehicles can also benefit the environment.
A study from the University of Michigan showed that self-driving vehicles reduce energy use and greenhouse gas emissions by up to 9%, when compared with traditional cars.
New Cars With Self-Driving Technology
Pretty much all new cars feature autonomous driver assistance software, like adaptive cruise control or automatic emergency braking.
However, the most sophisticated Level 2 self-driving features can be found in vehicles from Ford, General Motors, Mercedes-Benz, and Tesla.
Ford BlueCruise
BlueCruise is available in most new Fords and Lincolns and wowed consumers with its adaptive cruise control with lane-keeping technology. With this system, drivers can temporarily take their hand off the wheel, but they should still keep their eyes on the road ahead.
Ford BlueCruise (cont’d)
With BlueCruise, drivers can pre-map more than 100,000 miles of road in the car’s system, which helps with navigation. The software notifies drivers when it can be activated and can automatically steer the car.
Buyers will have to purchase a three-year subscription for BlueCruise—and get the right trim to use the software.
General Motors Super Cruise
The lane-keeping system that’s part of the Super Cruise software is smart enough to handle curves in the road and features an automatic braking system that can prevent collisions.
The software still requires drivers to focus on the road, and even has a monitoring system to watch your eyes and alert you if you’re not paying enough attention to the road.
General Motors Super Cruise (cont’d)
Super Cruise is available on several electric vehicles, like the Chevy Bolt, and on several Cadillac vehicles, including the 2024 Escalade. The first three years of the software are free, before requiring a subscription.
200,000 miles of North American roads are pre-mapped into the system by General Motors.
Mercedes-Benz Distronic Plus
The Distronic Plus is one of the more thrilling adaptive cruise control and lane-centering systems. Unlike other systems, it can handle high speeds, up to 120 mph, and will warn drivers if they’re about to be passed by another vehicle.
Many new additions to the Mercedes-Benz lineup also feature Parktronic software, which uses driver input to help the car self-park.
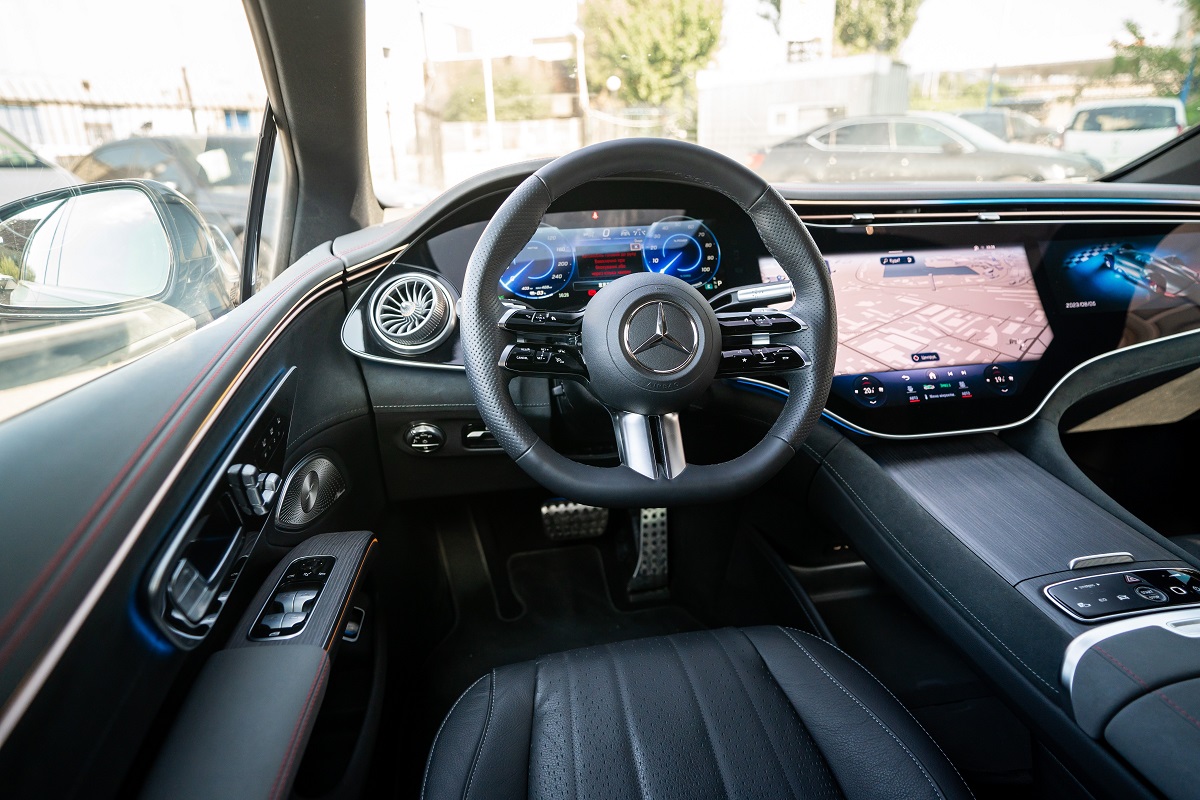
Mercedes-Benz Drive Pilot
Recently, Mercedes-Benz unveiled their Drive Pilot system. Up to certain speeds, this Level 3 autonomous driving software can completely take over from the driver, allowing them to take their eyes off the road.
The software will be available by subscription in the 2024 S-Class and EQS sedan.
 Dmitriy Sinchenko, Shutterstock
Dmitriy Sinchenko, Shutterstock
Tesla Autopilot
Tesla has long been a pioneer when it comes to self-driving cars. Their Autopilot software is a standard feature on all new models and uses an awareness of surrounding traffic to slow or accelerate the car to match the flow of traffic.
This is much like most other Level 2 systems, but this software can be upgraded to include Full Self-Driving.
 Natecation, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
Natecation, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
Tesla Full Self-Driving
With Full Self-Driving, the car can change lanes at high speeds, park itself, and back out of a parking space. There’s also an upgrade in development that would allow the car to automatically stop for traffic lights and navigate highway ramps.
Tesla’s Full Sel-Driving software was recently recalled, but the company has corrected the problems that were outlined by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration,
The Future Of Self-Driving Cars
According to consumer data, the interest in autonomous vehicles is steadily growing—and people are willing to shell out big bucks for these features.
By 2035, autonomous driving software is expected to be a $300 billion industry. By 2030, we can expect to see more passenger cars with Level 3 capabilities, or higher.
Final Thoughts
Self-driving cars are here to stay, but despite their popularity, advances in autonomous driving software are still really slow.
What we can achieve with the current Level 2 software has shown amazing benefits like increasing mobility for certain members of the population and reducing traffic congestion and greenhouse gas emissions. But it’ll still be a while before we can fully relinquish control of our cars.